All Types of Conjunctions with Examples: A Complete Grammar Guide
Conjunctions are powerful tools in English. They connect words, phrases, or clauses, making your writing smooth and meaningful. Without conjunctions, sentences would be choppy and ideas would feel disconnected. In this guide, you’ll learn all the main types of conjunctions with simple explanations and examples.
What Is a Conjunction?
A conjunction is a word used to connect parts of a sentence. These connections can happen between:
- Words (e.g., cats and dogs)
- Phrases (e.g., in the kitchen or on the table)
- Clauses (e.g., I wanted to go, but it was raining)
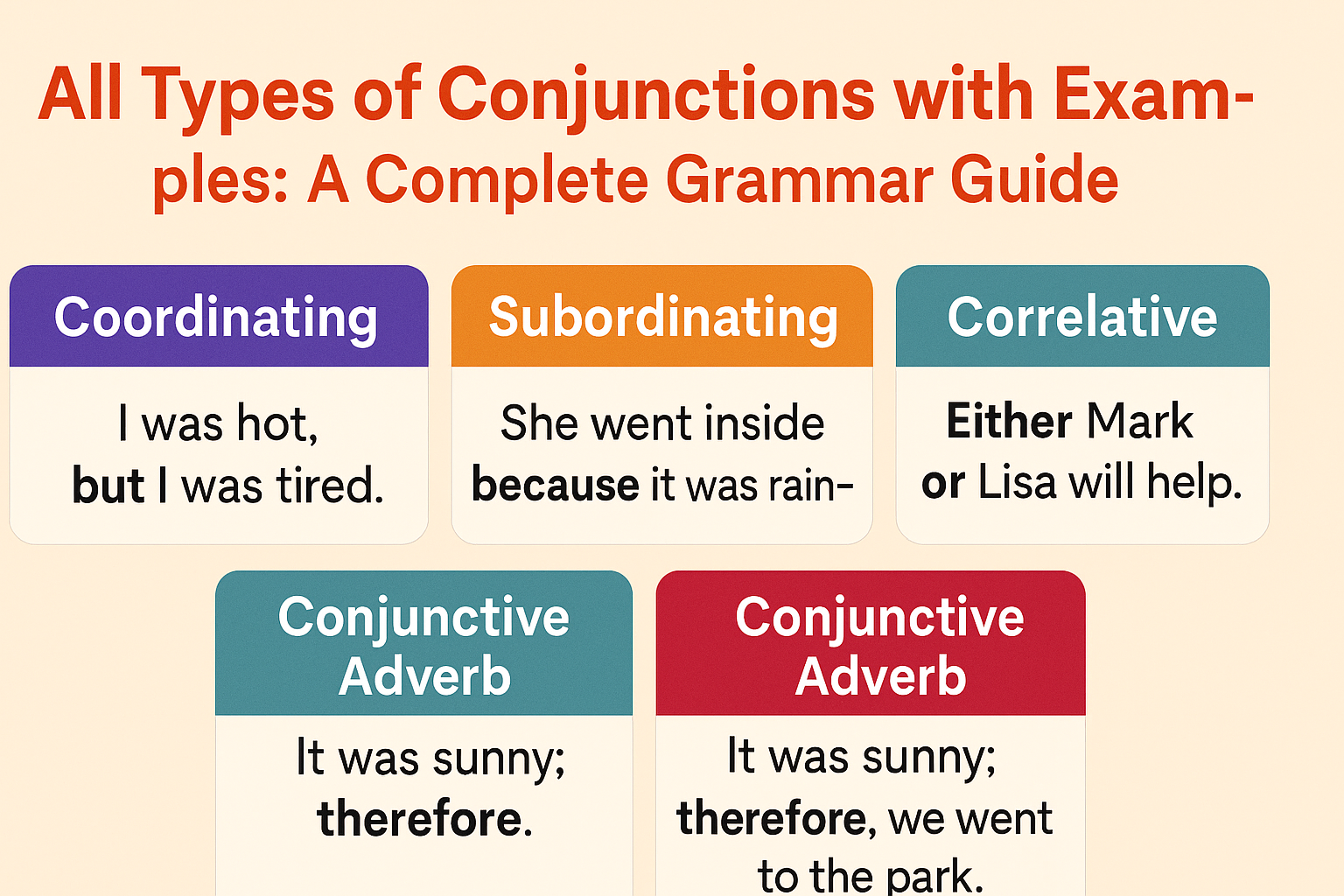
There are three primary types of conjunctions:
- Coordinating Conjunctions
- Subordinating Conjunctions
- Correlative Conjunctions
Let’s go through each type in detail.
1. Coordinating Conjunctions
These connect words, phrases, or independent clauses that are grammatically equal.
There are seven main coordinating conjunctions, easily remembered using the acronym FANBOYS:
- For
- And
- Nor
- But
- Or
- Yet
- So
Examples:
- I want pizza and pasta.
- She didn’t study, but she still passed.
- He was tired, so he went to bed early.
Each coordinating conjunction has its own function:
| Conjunction | Use | Example |
| For | Reason | She stayed home, for she was sick. |
| And | Addition | We bought apples and oranges. |
| Nor | Negative alternative | He doesn’t like tea, nor does he like coffee. |
| But | Contrast | I tried hard, but I failed. |
| Or | Choice | Would you like tea or coffee? |
| Yet | Unexpected contrast | It’s cold, yet sunny. |
| So | Result | I was late, so I missed the train. |
2. Subordinating Conjunctions
These connect an independent clause with a dependent clause. The dependent clause cannot stand alone and adds extra information.
Common subordinating conjunctions:
- Although
- Because
- Since
- If
- When
- While
- Unless
- After
- Before
- As
- Even though
- Until
Examples:
- Because it was raining, we stayed inside.
- We left early although the concert wasn’t over.
- I’ll call you when I get home.
- You can’t go out unless you finish your homework.
These conjunctions often appear at the beginning of complex sentences and introduce time, reason, condition, contrast, or place.
3. Correlative Conjunctions
These are pairs of words that work together to connect equal elements in a sentence.
Common correlative conjunctions:
- Either…or
- Neither…nor
- Both…and
- Not only…but also
- Whether…or
Examples:
- Either you come now or I’m leaving.
- She likes both swimming and running.
- Not only was the food delicious, but also the service was excellent.
- Neither Tom nor Jerry could answer the question.
Correlative conjunctions require balance. Make sure the parts being joined are of the same grammatical structure.
Conjunctions in Action: More Examples
Let’s look at how these conjunctions appear in everyday writing:
Coordinating:
- She wants to go hiking, but it’s too hot outside.
Subordinating:
- Although he was tired, he finished the project.
Correlative:
- Whether we win or lose, we’ll learn something valuable.
Tips for Using Conjunctions Effectively
- Avoid sentence fragments.
A subordinating conjunction creates a dependent clause. Don’t leave it hanging without the main clause.
❌ Because I was tired.
✅ I went to bed early because I was tired. - Watch your punctuation.
If a dependent clause starts the sentence, use a comma.
✅ Although it rained, we had fun.
✅ We had fun although it rained. - Use parallel structure with correlative conjunctions.
✅ She enjoys not only singing but also dancing.
❌ She enjoys not only singing but also to dance. - Don’t overuse conjunctions.
Too many can make your sentences run-on or confusing. Keep it clear and concise.
Summary Table: All Types of Conjunctions
| Type | Function | Examples |
| Coordinating | Joins equal words/phrases/clauses | and, but, or, so, yet, for, nor |
| Subordinating | Joins dependent to independent clause | because, although, since, if, when, unless |
| Correlative | Joins in pairs | either…or, neither…nor, not only…but also, both…and |
Final Thoughts
Understanding how conjunctions work helps you build strong, smooth, and grammatically correct sentences. Whether you’re writing essays, emails, or creative stories, the right use of conjunctions can improve clarity and flow.





