Affect vs. Effect: Know the Difference with Simple Examples
The words affect and effect are commonly confused in both writing and speech. They sound similar and are closely related in meaning, but they play different roles in a sentence. In this guide, we’ll explain the difference between affect and effect using simple explanations and examples.
The Core Difference
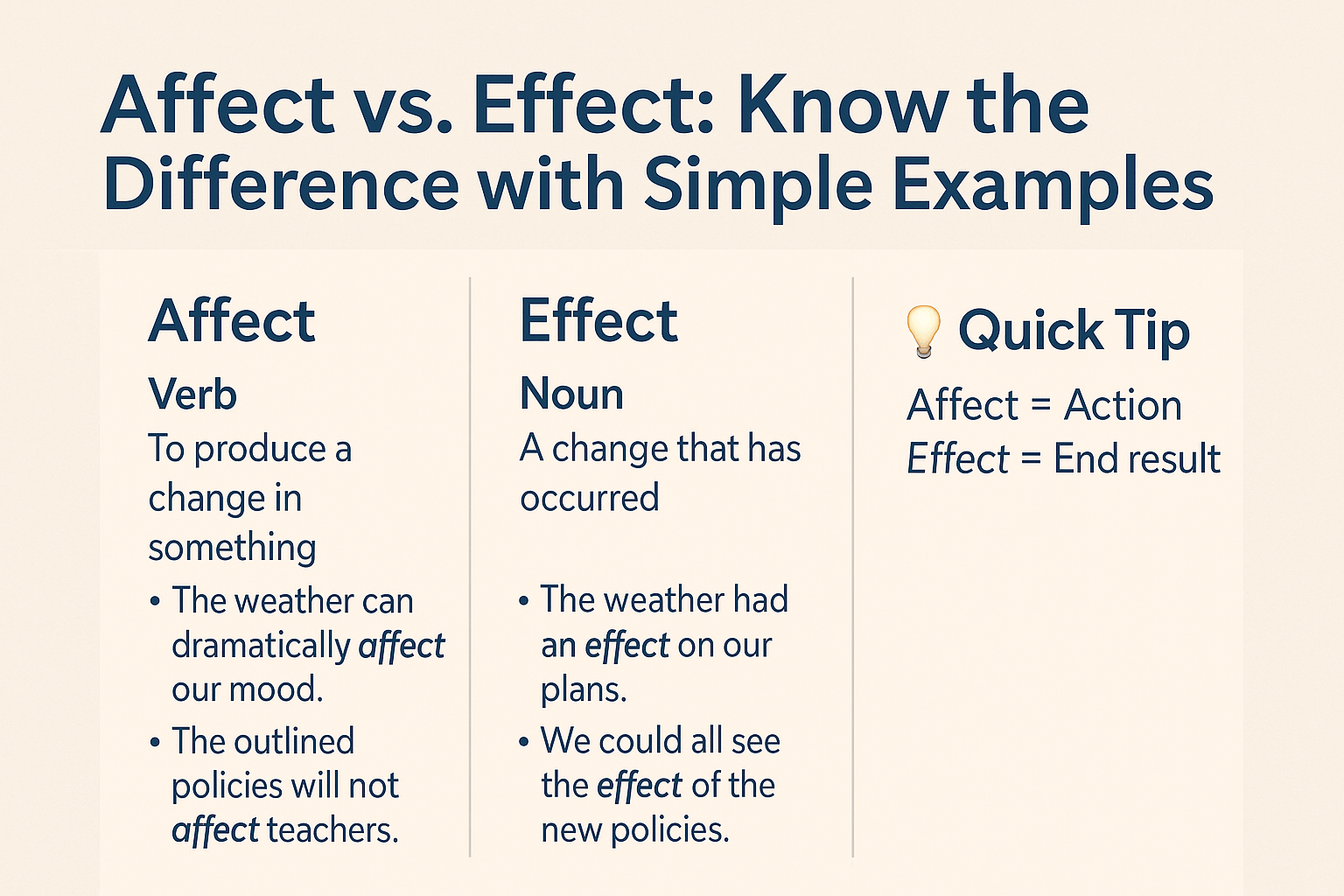
- Affect is usually a verb.
- Effect is usually a noun.
That’s the basic rule. Let’s break it down.
What Does “Affect” Mean?
When used as a verb, affect means to influence or make a change in something.
Examples:
- Weather can affect your mood.
- The loud noise affected my concentration.
- Lack of sleep can affect your health.
In all these sentences, “affect” is doing something—changing or influencing another thing.
What Does “Effect” Mean?
When used as a noun, effect means a result or an outcome.
Examples:
- The medicine had a calming effect.
- His speech had a powerful effect on the audience.
- One effect of the new policy is increased productivity.
In these examples, “effect” is something that happens because of something else.
Quick Tip to Remember
Here’s an easy memory trick:
- Affect = Action (verb)
- Effect = End result (noun)
Exceptions to the Rule
While affect is typically a verb and effect a noun, there are some exceptions where both words can switch roles.
“Effect” as a verb (less common):
When used as a verb, “effect” means to cause something to happen or bring about a result.
- The new manager will effect major changes in the company.
Here, “effect” is a verb meaning “to make something happen.”
“Affect” as a noun (rare and used in psychology):
In psychology, “affect” as a noun refers to a person’s emotional state or outward emotional expression.
- The patient displayed a flat affect during the interview.
This use is uncommon outside of psychology and mental health discussions.
Side-by-Side Comparison
| Word | Part of Speech | Meaning | Example |
| Affect | Verb | To influence or change | The news may affect your decision. |
| Effect | Noun | A result or outcome | The new rule had a positive effect. |
| Effect | Verb (rare) | To bring about | The board hopes to effect improvements. |
| Affect | Noun (rare) | Emotional expression | He showed little affect in his response. |
More Simple Examples
Let’s look at real-life examples to make the difference even clearer:
Affect (verb):
- The rainy weather affected the turnout at the event.
- Stress can negatively affect your immune system.
- Her attitude affects everyone around her.
Effect (noun):
- The sound effects in the movie were impressive.
- The new law had little effect on behavior.
- Positive thinking can have a big effect on your life.
Common Mistakes to Watch Out For
- ❌ “The weather had a big affect on my day.”
✅ Correction: “The weather had a big effect on my day.” - ❌ “This decision will effect your grades.”
✅ Correction: “This decision will affect your grades.”